Encardio Rite Borehole Vibrating Wire Extensometer is a specially designed instrument that assists civil engineers and geologists in the measurement of deformation of rock mass and adjacent or surrounding soil. Coupled with anchor bolt load cells and tape extensometer, it makes an essential geotechnical instrument for investigating and monitoring of foundations, slopes & embankments and for studying the behaviour of rock around underground cavities, tunnels, and mines.
Vibrating Wire Extensometer- Applications
- To predict the behaviour of a roof or wall of a mine, underground cavity, or tunnel during excavation.
- To forecast a potential roof or wall fall before their occurrence as they are preceded by measurable sags as the strata open up and the movement usually occurs at an increasing rate as fall conditions are approached.
- Extensometers are used to estimate and monitor the movements in slopes and foundations that occur due to the excavation of underground cavities or due to the construction of heavy structures like concrete, rockfill, masonry, or earth dams over the foundation.
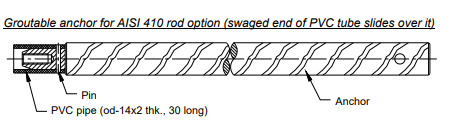
- Suitable for upward or downward-sloping holes using fibreglass or stainless steel AISI-410 connecting rods.
Encardio Rite Model EDS-70V Features:
- Three extensometers can be mounted in a borehole of 76 mm. The diameter at the mouth of the borehole is increased to 90 mm (300 mm depth for a 50 mm displacement sensor or 430 mm depth for a 100 mm displacement sensor).
- Provision for mounting up to six extensometers in a borehole of 102 mm. The diameter at the mouth of the borehole is increased to 125 mm (300 mm depth for 50 mm displacement sensor and 430 mm depth for 100 mm displacement sensor).
Borehole Vibrating Wire Extensometer is used to measure the displacement that takes place in a bored hole or several bored holes in a rock mass, with respect to time. It is equipped with one or more anchors and a reference plate.
Anchors are usually placed in the same borehole or drilled adjacent to the first borehole in case of placing them in different boreholes.
The Borehole Extensometer assists in measuring the distance between various anchors with respect to the reference plat and thus helps monitor with time their relative displacement in respect to each other.
It is usually assumed that the deepest anchor is in the stable ground and so any change in anchor spacing is interpreted as sag of roof bed, movement of sidewall or slope, settlement of foundation, etc.
Encardio Rite EDS-70V Vibrating Wire Extensometer can be mounted in a borehole and the displacement is monitored with the help of vibrating wire displacement sensors.
At places where access to the mouth of the borehole is easily available, mechanical displacement measurement is economical and reliable, with displacement reading taken by a micrometer depth gage that measures the depth of the reference button at the near end of the connecting rod from a reference plate.
Model EDS-70V borehole vibrating wire extensometer comprises four major sub-assemblies:
- Reference head assembly
- Vibrating wire displacement sensors
- Connecting rod assembly (fibreglass or stainless steel AISI 410)
- Anchor (reinforced bar or packer)
Reference Head Assembly
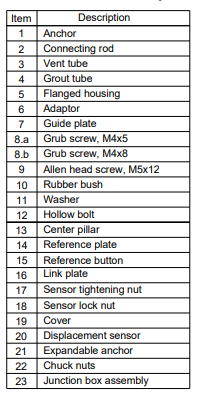
The Reference head assembly consists of the list of items listed in the image above.
The sensors are supplied separately and can be easily installed on-site inside the reference head assembly with the connecting rod ends.
The reference head assembly is designed with flanged housing which has an adaptor fixed at one end with the help of M4 x 5 grub screws (8a).
A guide plate is attached to the M5 x 12 Allen head screws (9).
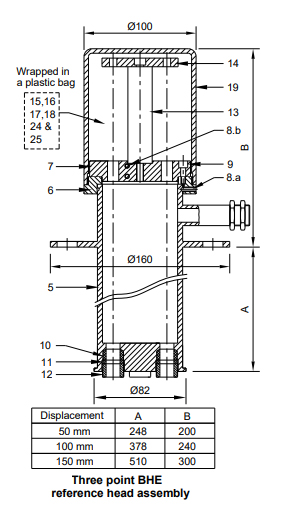
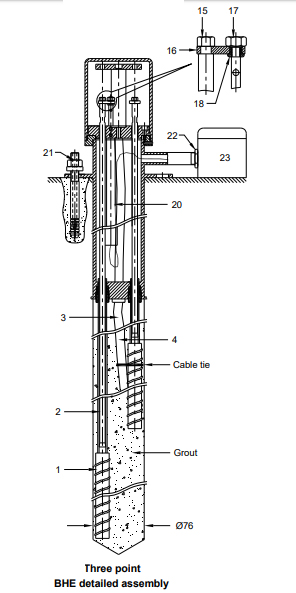
In the case of a three-point borehole vibrating wire extensometer (BHE), the reference plate is secured to the guide plate with the help of four stainless steel spacers (13). On the other hand, in the case of six-point BHE, it is fixed through a center pillar (13).
The holes of the guide plate and reference plate are marked correspondingly in a clockwise manner starting from the number “1”. Similarly, the corresponding holes of the guide plate and reference plate are marked ‘G’ and ‘V’ for the grout and vent tube.
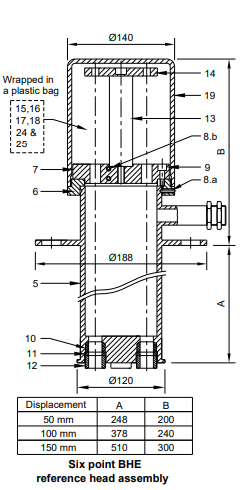
The removable cover is strung to the guide plate. In case you require less than 3/6 points, the other points are plugged with the help of a standard rubber plug, steel washer, and hollow bolts.
Vibrating Wire Displacement Sensor
Model EDS-70v Vibrating Wire Extensometer uses an Encardio Rite Model EDE-VXX linear displacement sensor to transmit mechanical displacement to a remote observation room.
It consists of a vibrating wire sensor having a stroke of 50 or 100 mm. A male thread of M6 x 12 is present on the retractable shaft of the sensor to which the connecting rod can be attached through a link system.
The sensor is equipped with a 1 m long 4 mm four-core cable with cores in red, black, green, and white. Red and black cores are used for frequency signals, while green and white monitor temperature through a thermistor.
Connecting rod assembly
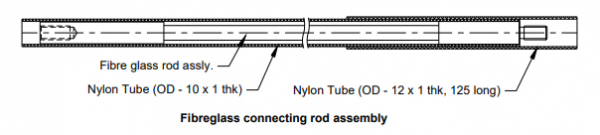
Fibreglass connecting rod assembly
Fibreglass connecting rod assembly (2) comprises a fibreglass rod of specified length protected inside an outer continuous nylon tube.
The fibreglass connecting rod assembly has two ends connected. The connector with the male thread fits into the anchor, while the other end of the connector with the female thread is connected to the reference button. Displacement of the connecting rod is transferred through a link plate (16) to the displacement sensor (20) with the help of a sensor tightening nut (17) and a sensor lock nut (18).
Components 15, 16, 17, and 18 are packed inside the reference head assembly in a plastic bag.
An end of the nylon tube is securely attached with an anchor to avoid any leaking. The other end of the nylon is firmly sealed in reference head assembly with the help of a rubber bush (10), washer (11), and hollow bolt (12).
The sealing is extremely important in upwards to horizontally slant holes as it prevents any grout from leaking into the reference head assembly during grouting. The covering of the nylon tube enables the fibreglass rod and reference button to move freely even after the borehole is grouted.
Stainless steel AISI 410 connecting rod assembly
The stainless steel rods are accessible in standard lengths of 1m, 2 m, and 3 m with an M6 x 12 mm male thread at one end and an M6 x 15 mm female thread at the other end.
They are combined together on-site to position the anchor at the accurate depth from the mouth of the borehole. The threads are tightly bound together with the help of thread sealant Loctite 577 or equivalent.
For example, in case the depth of a particular anchor from the mouth is 14 m, use four connecting rods of 3 m length and one of 2 m length. Similarly, in case the depth of the anchor from the mouth is 25 m, use eight connecting rods of 3 m in length and one connecting rod of 1 m.
A standard 14 cm spacer with male thread on one side and female on the other side is always given at the near end of the assembled connecting rods. The reference button is attached to the female end of the space.
A sensor tightening nut (17) and a sensor lock nut (18) are used to transfer the displacement of the connecting rod end through a link plate (16) to the displacement sensor (20).
Components 15, 16, 17, and 18 are packed inside the reference head assembly in a plastic bag. The most distant male thread of the connecting rod fits into the anchor.
PVC tubing 14 mm OD x 10 mm ID in 3 m length is provided for enclosing connecting rods at the time of assembly.
One end of these tubes is swaged to make the male extender that allows the male and female ends of successive PVC tubes to be conveniently joined using any PVC jointing compound in between. Once the process is done, the joint is verified by pulling and is wrapped with PVC tape to avoid any leakage.
The outer PVC tubing allows free movement to connect rods and reference buttons even after the borehole is grouted. The PVC tubing furthest away from the mouth of the borehole is tightly fastened to the anchor to avoid any grout leakage. To join successive connecting rods and PVC tubing, this 3 m long PVC tubing is cut by 50 mm from the plain end.
The near end of the PVC tubing is tightly sealed in flanged housing (5) with the help of a rubber bush (10), washer (11), and hollow bolt (12). Make sure to cut the PVC Tube in such a manner that its face extends around 20 mm beyond the rubber bush (20).
The sealing is extremely important in upwards to horizontally slant holes as it prevents any grout from leaking into the reference head assembly during grouting.
Anchor
Encardio Rite deals with the following types of Anchors:
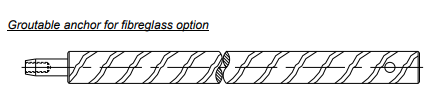
- Encardio Rite groutable anchors 20 mm x 500 mm long usually used for hard rocks. These are inserted into the borehole with a connecting rod of a suitable length and then set in position by cement grout. The connecting rod is free to move as it is covered in plastic tubing.
Groutable anchors are installed in vertical boreholes or holes inclined upwards. When installing in holes inclined upwards, special precautions have to be taken to retain the grout and prevent it from flowing out of the borehole.
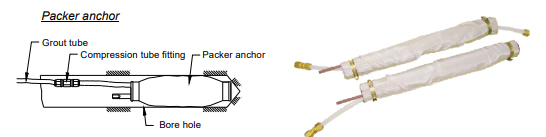
The other type of anchors- packer anchors are used for soft rocks and soil. These are lowered down or pushed in the borehole along with a connecting rod of appropriate length and fixed in position by pumping cement grout into the packer for taking a firm grip on the surroundings.