The inclinometer is a geotechnical instrument that is used to measure the angle of inclination or tilt of an object concerning gravity’s direction. We use the output to determine the variation with time in structures like retaining walls, diaphragms, and many more. In this article, we will be looking at the working, application, and features of Encardio Rite Wireless in-place Inclinometer.
Encardio Rite is one of the most renowned and leading manufacturers and suppliers of inclinometers. They have a robust collection of sensors that boasts of accuracy, reliability, and modern technology.
Wireless In-place Inclinometer – Introduction

Encardio Rite Model EAN-53MW is one of the most advanced and accurate wireless in-place inclinometer systems available in the market today. It is specially curated to measure lateral movements of earthwork and other structures. The Inclinometer finds its application in places where real-time monitoring is used to present early signs of warning and gives enough time to take the required safety measures.
The Wireless IPI is a collection of inclination sensors equipped with an SDI-12 digital interface, that are placed inside an inclinometer gauge well. This entire instrument is connected to a wireless mesh network with Node and Gateway, making real-time monitoring a possibility. The use of a wireless mesh network allows data to transfer over long distances without any lag or delay. On the other hand, with data logging and real-time monitoring features, you can instantly provide early warning and avoid any casualties.
Wireless In-place Inclinometer – Features
- It provides accurate, reliable, and high-resolution reading with long-term stability.
- IPI is designed with the most sturdy and robust construction
- Get seamless connectivity in large sites with the help of the wireless mesh-based data collection protocol.
- Excellent temperature stability
- The IPI is very simple to install and monitor even hard to access sites and tunnels.
Wireless In-place Inclinometer – Application
- Wireless IPI is helpful to accurately measure the lateral movement of structures, embankment fills, landslide areas above dams, highways, earthworks, etc.>
- It is used to monitor the deformation of embankments, retaining walls, etc.
- It finds its usage in stability investigation, construction control, and ground movement monitoring that is a result of tunnel construction or any such excavation.
The In-place inclinometer is especially used to measure and provide quantitative data on the magnitude of inclination or tilt of a foundation, embankment, or slope and its variations with time. The instrument helps to identify the pattern of deformation, the danger zones, as well as the effectiveness of construction control measures. The geotechnical instrument is also used post-construction to observe the behavior of ground movement. This helps to identify any potential danger or mishap that may hurt the stability of the structure, its foundation, and its appurtenant.
Read More: Inclinometer: Types, How It Works, & Uses
Specification
| Sensor |
| Sensor | Uniaxial or biaxial sensor; with SDI-12 or without SDI-12 |
| Measuring Range | ± 15° |
| Accuracy | ± 0.1% fs |
| Temperature Limit | -20° to -80° C |
| Transmission Distance | Up to 15 km (line of sight)
Up to 4 km (cities, urban)
Up to 3 km (tunnels, underground) |
| Power Supply | 12 V DC @ 2A nominal, Solar panel |
| Battery | 1 D-cell Lithium Thionyl Chloride (Li-SOCl2) 3.6 V 19 Ah batteries. |
| Radio Frequency |
| Transmission distance | Up to 15 km (line of sight)
Up to 4 km (cities, urban) |
| Radio bands | Sub-1 GHz band – complies with unlicensed ISM band specifications in most countries |
| Link data speed | 625 bps – 2.5 kbps variable bitrate |
| Data security | AES128 Encrypted end-to-end data |
| Gateway |
| Power supply | 12 V DC @ 2A nominal, Solar panel |
| Battery | 1 D-cell Lithium Thionyl Chloride (LiSOCl2) 3.6 V 19 Ah batteries. |
| Typical current drain | 200 mA typical operating current |
| Internal Connectivity | In-built 3G/4G modem, Ethernet |
Wireless In-place Inclinometer – System Description
It starts with a series of inclinometer access tubes, which are attached. They are then installed in a borehole or embedded in earth/rockfill or concrete structure during construction or can even be fixed to the vertical side of a finished structure. The in-place inclinometer consists of a series of inclination sensors with MEMS tilt sensors and an SDI-12 digital interface. This whole system is then placed inside the inclinometer casing to cover the movement zone.
The in-place inclination sensors are equipped with a pair of pivoted sprung wheels. Whereas, the rods connecting the sensors can be customized to match individual gage length requirements. You can easily place the sensors in areas that are subjected to movements. In case only a specific portion of the borehole needs monitoring, suspension stainless steel wire rope is provided to position a single or a group of sensors.
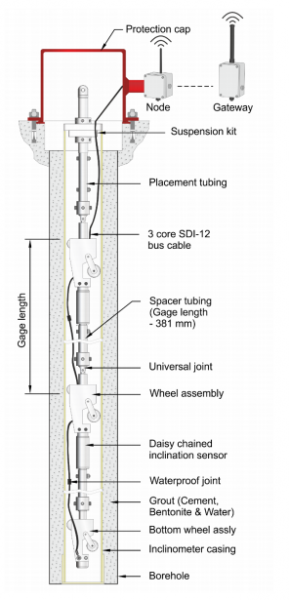
The system makes use of a single 3 conductor cable that is attached in a daisy chain fashion, connecting each sensor to the next, and then finally to the top of the borehole. It is also connected to the wireless communication network through a node.
This innovative design and connection of sensors allow each sensor to move independently without any influence. This provides a profile of displacement over the complete length of the installation.
Operation
Let’s see how the Wireless in-place inclinometer works.
When there is a movement in the ground, it displaces the inclinometer access tubing, which in turn leads to a change in the tilt of the IPI sensors. This is reflected as a change in the output of the sensors, proportional to the tilt i.e. the angle of inclination from the vertical.
The measured tilt reading is applicable over the gauge length(distance between the wheels) of the sensors. The reading can be converted to lateral deviation – “L sin θ” where L is gage length and θ is the angle of tilt from vertical.
The lateral movement of the casing can be measured by deducting the initial deviation from the current deviation.
If one end of the access tubing is secured, you can get a complete profile of the tubing by summing up the readings of successive sensors. The horizontal displacement of the gage well at different depths over some time can be determined by comparing these profiles.
Read More: Digital Inclinometer System: Introduction & How Does It Work
Wireless Mesh Network
The Wireless In-place Inclinometer is interfaced with the long-range, low-power wireless mesh network through a Node. This permits the sensors to send recorded data to the Gateway with over 99% reliability. The Gateway, in turn, uploads the data on a central/cloud server which can be accessed by an authoritative person.
The wireless mesh-based data collection method allows for seamless and smooth connectivity even in the most remote and large sites and tunnels
The system is low-power and consists of long-range wireless radios that provide a range of up to 15 km in each hop of the mesh network.
To manage the network, you can use cloud-hosted data management and configuration software. They are easy to configure and can be used with the smartphone application that comes with the system. The app is designed to provide the user with step-by-step instruction, as well as displays all the information regarding radio signals or battery strength.
You can use the database management system to analyze and visualize the data collected from the project site/installation locations. The data is accessible 24 x 7 to all the related authorities. The system is capable of producing automatic reports and sending alerts over SMS and email when any reading crosses the predefined alert levels.
Even if there are several sensor arrays/Nodes present at the site, the innovative mesh network ensures that the data from all of them are transferred to the Gateway, and from thereon to the cloud server without any delay. The mesh network works efficiently even if a node cannot reach the Gateway directly. You can still send the data to the Gateway via other Nodes in the network. The mesh network allows the Nodes to communicate with one another, and therefore they can relay other Node data to the Gateway.
The mesh network is designed to mitigate well-known wireless issues like signal blockages and interference, allowing the Inclinometers to reliably send their data to the gateway every time. The Radio Transmission in the system is secured via AES-128 encryption, ensuring maximum security of the sensor data gathered by the system.
This brings us to the end of our article on Wireless In-place inclinometer. Hope this was helpful. In case of any doubt or questions, feel free to comment below.